How Diet Affects Psychological and Physical Health?
How Diet Affects Psychological and Physical Health?
How do diets affect metabolism?
How we eat can have a profound effect on our metabolism. Our metabolism is the process by which our bodies convert food into energy. A slow metabolism can lead to weight gain[1], while a fast metabolism can help us maintain a healthy weight.
Certain foods can help to boost our metabolism,
while others can slow it down. For example, Junk foods
[2] tend to be slowly metabolized by the body, while complex carbs and protein are metabolized more quickly.
Eating smaller meals more often can also help to increase our metabolism, as our bodies have to work harder to digest the food. So, if we’re looking to boost our metabolism, we should focus on eating whole, unprocessed foods and spacing out our meals throughout the day.
Physical health and diet
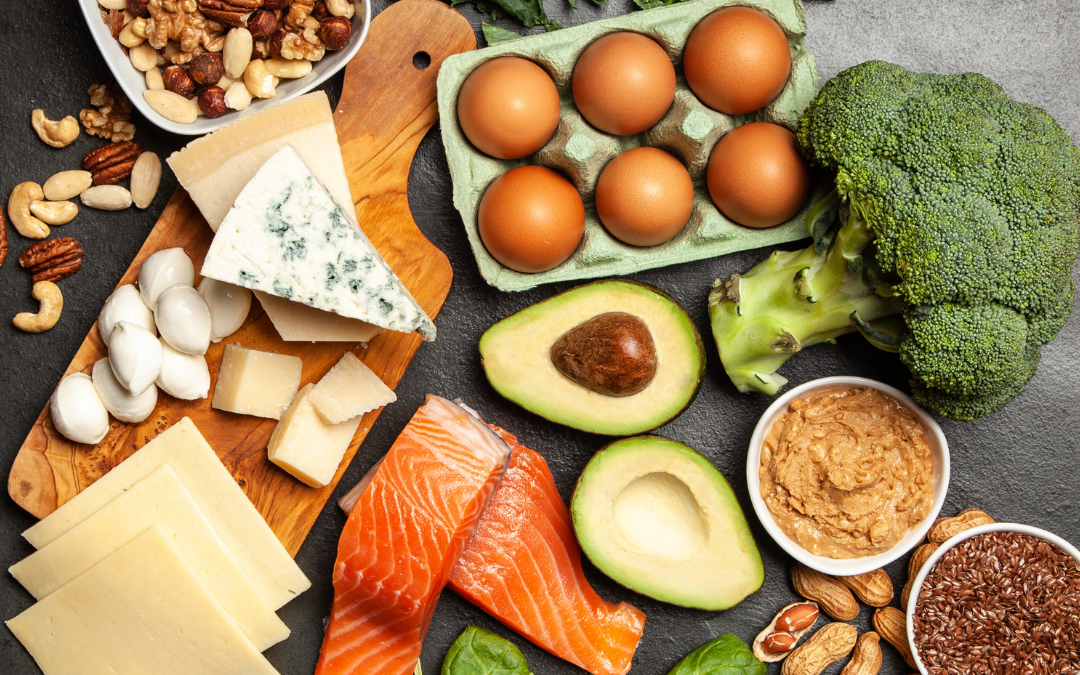
It’s no secret that diet plays a major role in physical health. The food we eat provides our bodies with the energy and nutrients they need to function properly. Eating a healthy diet[3] can help reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Conversely, consuming an unhealthy diet[4] can have negative effects on physical health. For example, eating too much processed food can lead to weight gain, while not getting enough fruits and vegetables can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
Making dietary changes can be difficult, but the benefits are clearly worth it. By incorporating more healthy foods into your diet, you can enjoy improved physical health.
Psychological health and diet
There is a growing body of research[5] that suggests that what we eat can have a profound effect on our mental health.
For example, studies [6] have shown that people who consume a diet high in processed foods and low in fresh fruits and vegetables are more likely to suffer from depression and anxiety.
Furthermore, research has linked certain nutrients to Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), which is a protein that helps to support the growth and maintenance of nerve cells.
Low levels of BDNF[7] have been associated with depression, so eating foods that are rich in BDNF-boosting nutrients (such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins B6 and B12, and folate) may help to improve mood.

dentures
ReplyDeletedenturist
hearing aids
denture repairs,
denture relines,
facial prosthetics,
implant dentures,
flexible dentures,
night guard,
hearing test,
custom ear plugs,
full dentures,
partial dentures,
orbital prosthetics,
nasal prosthetics,
auricular prosthetics,
AR Smart Glasses
ReplyDeleteCameras
Desktops
Laptops
Monitors
PC Accessories
PC Components
Software
Storage Arrays
Tech Toys
VR Accessories
VR headsets
Create a business plan
Develop a marketing strategy
Create a brand identity
Identify new verticals
Improve workflow
Increase your online presence
AR Smart Glasses
Cameras
Desktops
Laptops
Monitors
PC Accessories
PC Components
Software
Storage Arrays
Tech Toys
VR Accessories
VR headsets
Inventory
ReplyDeleteRental Rates
Locations
Corporate Branding
Press & Contact
Inventory
Rental Rates
Locations
Corporate Branding
Press & Contact
Inventory
Rental Rates
Locations
Corporate Branding
Press & Contact
Inventory
Rental Rates
Locations
Corporate Branding
Press & Contact
Inventory
Rental Rates
Locations
Corporate Branding